SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Profiling Kit
SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Profiling Kit
SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Profiling Kit—capturing complete V(D)J variable regions of BCR transcripts
The new SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Profiling Kit pairs 5' RACE with NGS technology to provide a sensitive, accurate, and optimized approach to BCR profiling from RNA input samples. The 5' RACE method reduces variability and allows for priming from the constant region of BCR heavy or light chains. This kit combines these benefits with gene-specific amplification to capture complete V(D)J variable regions of BCR transcripts and provide a highly sensitive and reproducible method for profiling B-cell repertoires.
The kit is designed to work with a range of RNA input amounts depending on the sample type, and has been shown to generate high-quality, Illumina-ready libraries from as little as 10 ng to 1 µg of total RNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and 1 to 100 ng of total RNA from B cells. Data can be generated for both heavy and light chains (kappa and lambda) of human immunoglobulin IgG and IgM. This latest profiling kit also includes unique molecular identifiers (UMI), making it possible to remove reads derived from PCR errors or duplication and/or sequencing errors, thus ensuring more accurate and reliable results
Overview
- Input: 10 ng to 1 µg of total RNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or 1 to 100 ng of total RNA from B cells
- UMI-based correction for removal of reads derived from PCR error or duplication and/or sequencing errors
- Sensitive and specific clonotype detection with optimized cDNA library generation
- Accurate amplification of human IgG subclasses and identification via sequencing in a majority of cases
- Optimized PCR pooling strategy for highly sensitive detection of different chains from the same sample
- Flexible pooling strategies accommodate different experimental requirements regarding alignment and identification of primary chain sequences
Applications
- Human BCR repertoire analysis (heavy and light [kappa and lambda] chains)
SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Profiling Kit Workflow
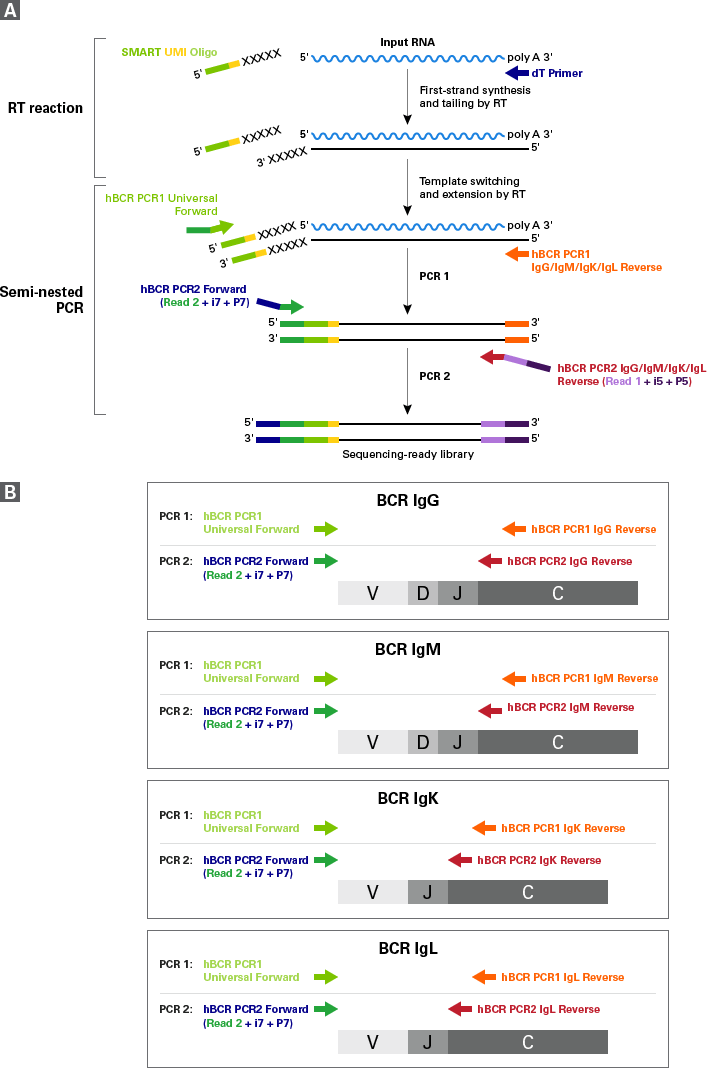
Figure 1. SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Profiling Kit workflow. Panel A. First-strand cDNA synthesis is dT-primed and performed by the MMLV-derived SMARTScribe Reverse Transcriptase (RT), which adds nontemplated nucleotides upon reaching the 5' end of each mRNA template. The SMART UMI Oligo anneals to these nontemplated nucleotides and serves as a template for the incorporation of an additional sequence of nucleotides into the first-strand cDNA by the RT (this is the template-switching step). The first strand cDNA is then subjected to two rounds of gene-specific PCR amplification (see details in panel B). The nested PCR in the second round ensures that the vast majority of the reads map to B-cell receptor transcripts. Panel B. The first PCR uses the first-strand cDNA as a template and includes a forward primer with complementarity to the Illumina Read Primer 2 sequence (PCR1 Universal Forward primer), and a reverse primer that is complementary to the constant region of BCR heavy or light chains (PCR1 IgG/IgM/IgK/IgL Reverse primers). By priming from the Read Primer 2 sequence and the constant region, the first PCR specifically amplifies the entire variable region and a considerable portion of the constant region of BCR heavy or light chain cDNA. The second PCR takes the product from the first PCR as a template and uses semi-nested primers (PCR2 IgG/IgM/IgK/IgL Reverse primers) to amplify the entire variable region and a portion of the constant region of BCR heavy or light chain cDNA.
Sensitive and reproducible clonotype detection from a wide range of RNA amounts

Figure 2. Clonotype calls identified from 1–100 ng B-cell RNA. BCR profiling IgG, IgM, IgK, and IgL libraries were generated from 1 ng, 10 ng, and 100 ng of human CD19+ B-cell total RNA. For analysis, libraries were downsampled to 100,000 reads, 400,000 reads, and 5,000,000 reads for RNA inputs of 1 ng, 10 ng, and 100 ng, respectively, then processed by the Takara Bio Immune Profiler Software.
Confident identification of low-abundance clonotypes
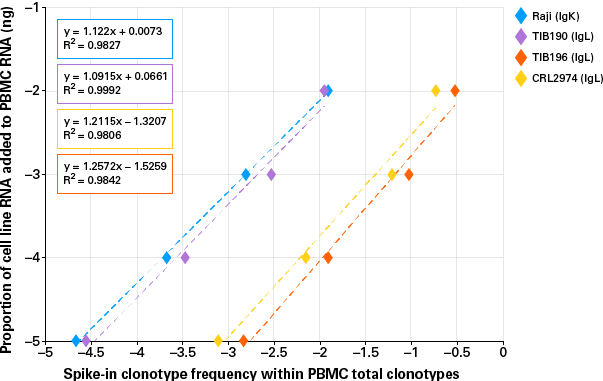
Figure 3. Successful identification of low-abundance clones. 1 ng, 100 pg, 10 pg, and 1 pg of each of the four cell lines (Raji, TIB190, TIB196, and CRL2974) were spiked into 100 ng of a single donor's PBMC RNA. The plot above shows calculated correlations between spike-in RNA proportions (Log10) and detected frequencies (Log10) for each cell line.
Significant impact of biological variation on the number of clonotypes detected

Figure 4. Clonotype counts from PBMC RNA obtained from different donors. IgG, IgM, IgK, and IgL clonotypes from 10 ng each of PBMC RNA from eight donors (represented by different colors) were determined using the SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Profiling Kit. Libraries were normalized to 100,000 reads for analysis.
Avoid oversequencing with UMI analysis
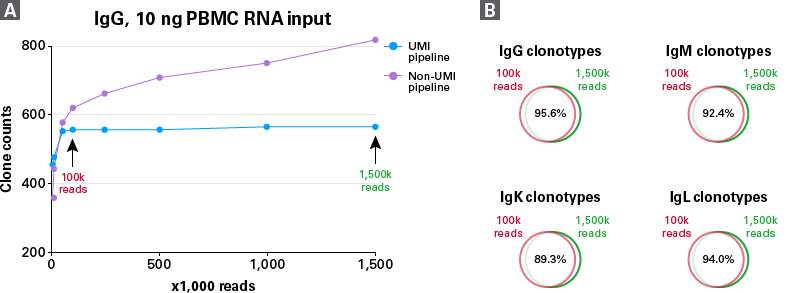
Figure 5. Evaluation of sequencing saturation for 10-ng PBMC RNA libraries. BCR profiling libraries from 10 ng of PBMC RNA from a single donor were prepared using the SMARTer Human BCR IgG IgM H/K/L Kit. Panel A. IgG clonotype counts at different sequencing depths are shown with (blue line) and without (purple line) UMI-based error correction. IgG and other chains (IgM, IgK, and IgL not shown) were sequenced at 1.5 million reads per library, then were downsampled to 1 million, 500K, 200K, 100K, 50K, 10K, and 5K reads. All analyses at different sequencing depths were generated with our Takara Bio Immune Profiler Software. Panel B. Venn diagrams showing overlapped clonotypes between libraries with low (100K) and high (1,500K) sequencing depths.