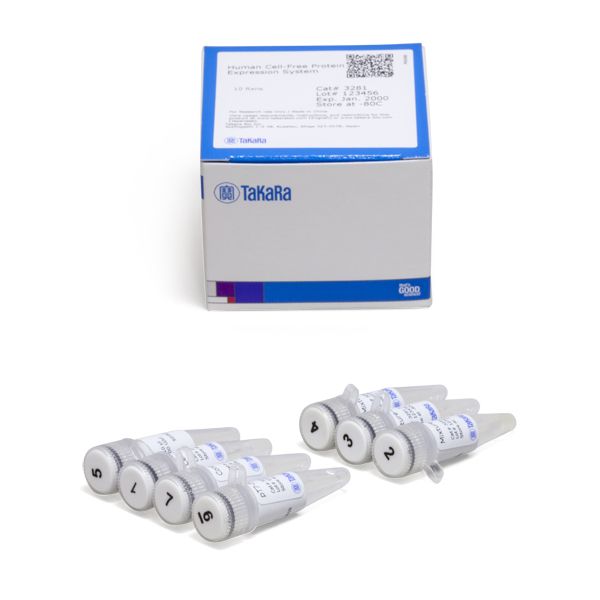
Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System
Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System
The Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System from Takara Bio is easy to use. The single-tube reaction is easily assembled and protein synthesis is complete in as little as 1 hr at 32°C. The Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System provides high yield (e.g., 50 μg/ml of human eIF4G) of functional protein, including proteins requiring modifications such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, or fatty acylation and even with large proteins (over 150 kDa). Genes of interest may be cloned rapidly into pT7-IRES vectors using In-Fusion cloning technology. After expression, proteins with N-terminal or C-terminal His tag or N-terminal Myc tag can be generated, depending on choice of vector.
Overview
- Easy-to-use system allows generation of protein in as little as 1 hour in a single-tube reaction
- Provides higher yield and greater consistency of functional protein compared to rabbit reticulocyte in vitro translation systems
- Works well with challenging applications such as large proteins (over 150 kDa)
- Amenable to high-throughput screening; bulk sizes are available
Applications
- Expression of toxic proteins that are lethal for in vivo expression systems
- Quick analysis of protein functionality
- Rapid analysis of protein mutations or truncations
- Expression of proteins that are easily degraded or insoluble in conventional in vivo expression systems such as E. coli
- High-throughput proteomic studies
Principle of the Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System

Principle of the Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System. A) In an easy and simple protocol, target protein translation is initiated by adding pT7-IRES Vector containing the target gene cassette and other kit components. B) The target gene RNA transcribed from the pT7-IRES Vector has an IRES sequence designed to promote protein translation initiation. As protein synthesis progresses, the translation initiation factor from the cell lysate becomes inactivated. The translation enhancement factor in the reaction mixture, however, reactivates this inactivated translation initiation factor and thereby maintains high translation level.
Time course of beta-galactosidase expression and effect of translation enhancement factor

Time course of beta-galactosidase expression and effect of translation enhancement factor. Eight replicates of beta-galactosidase in vitro translation were performed using 1 µl of Control Vector per reaction. At each of the indicated time points (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4.5, 6, and 8 hours after start of the reaction), one reaction tube was removed and used for beta-galactosidase activity assay with O-nitrophenyl-b-D-galactopyranoside (ONPG) as the substrate. A separate set of reactions were conducted in absence of the translation enhancement factor (Mixture-2). The activity of beta-galactosidase increased over time to peak at approximately 4.5 h. Additionally, the presence of Mixture-2 containing translation enhancement factor markedly increased yield of active protein.
Synthesis of high molecular weight proteins using the Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System

Synthesis of high molecular weight proteins using the Human Cell-Free Protein Expression System. In vitro translation reactions were performed to synthesize human Dicer (200 kDa, lane 2) or human eIF4G (170 kDa, lane 3) protein. Reactions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and coomassie blue staining. Arrowheads indicate target proteins. Lane 1, negative control.