Plasmid DNA purification - The Macherey-Nagel Way
Where do plasmid DNA impurities derive from?
Salts derived from purification procedures as well as proteins from the bacterial cells can lead to plasmid DNA contamination and poor downstream application results. Salts as well as proteins are efficiently depleted by MACHEREY‑NAGEL plasmid purification products. In addition, all our kits for plasmid DNA isolation contain RNase to avoid RNA contamination.
However, the majority of impurities in plasmid DNA preparations derive from endotoxins. Endotoxins are lipopolysaccharides from the bacterial cell wall that might be co-purified with the plasmid DNA. MACHEREY‑NAGEL provides plasmid isolation products that enable the efficient removal of endotoxins.
How do endotoxins affect downstream applications?
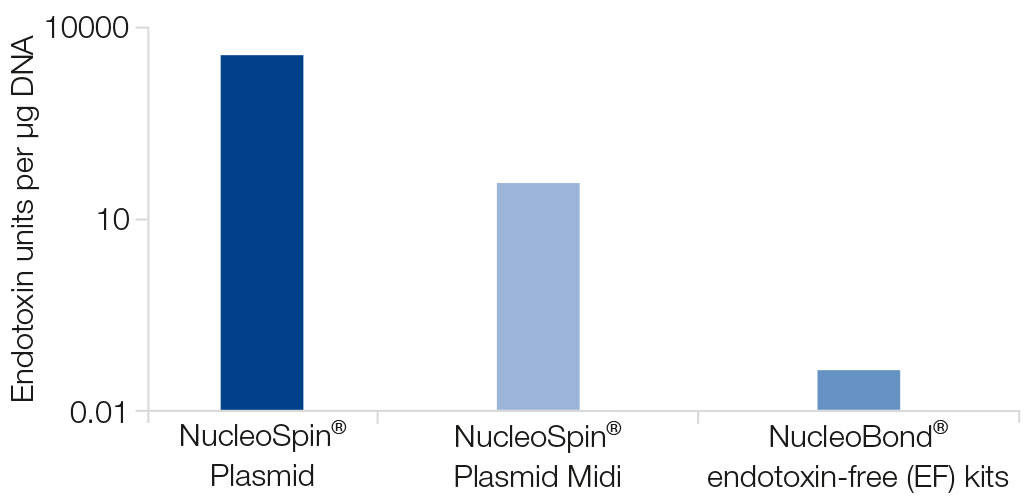
Endotoxins have cytotoxic effects and negatively influence cell viability and transfection efficiency. Additionally, endotoxins are known to influence gene expression in cell cultures, leading to false results in gene expression analyses. Endotoxin levels are measured by a standardized test, and the measurement unit is EU (endotoxin unit).
How to pick the right product?
The plasmid purification product that best fits your needs will depend upon your downstream application. Routine molecular biology applications are not influenced by the presence of endotoxins. However, manipulation of standard eukaryotic cell lines such as HeLa or HEK cells require a higher purity. For these applications, we recommend our transfection-grade plasmid DNA isolation kits with endotoxin levels between 1–50 EU/μg DNA. For highly sensitive applications, we recommend our endotoxin-free kits. These applications include the transfection of precious cell lines, such as primary cells, stem cells or cells growing in low numbers. Our endotoxin-free products enable the isolation of plasmid DNA with endotoxin levels below 0.1 EU/μg DNA.
Purification Technologies
NucleoSpin
- Technology: Silica membrane
- Formats: Mini spin column, 8‑well strip, 96‑well plate
- Processing: Vacuum or centrifugation
NucleoBond
- Technology: Anion exchange chromatography
- Formats: Mini to preparative scale columns, 96‑well plate
- Processing: Gravity flow
- (NucleoBond PC Prep 100 intended for HPLC, FPLC)
NucleoSnap
- Technology: Precipitation and filtration
- Format: Snap off column
- Processing: Vacuum (centrifugation for elution)
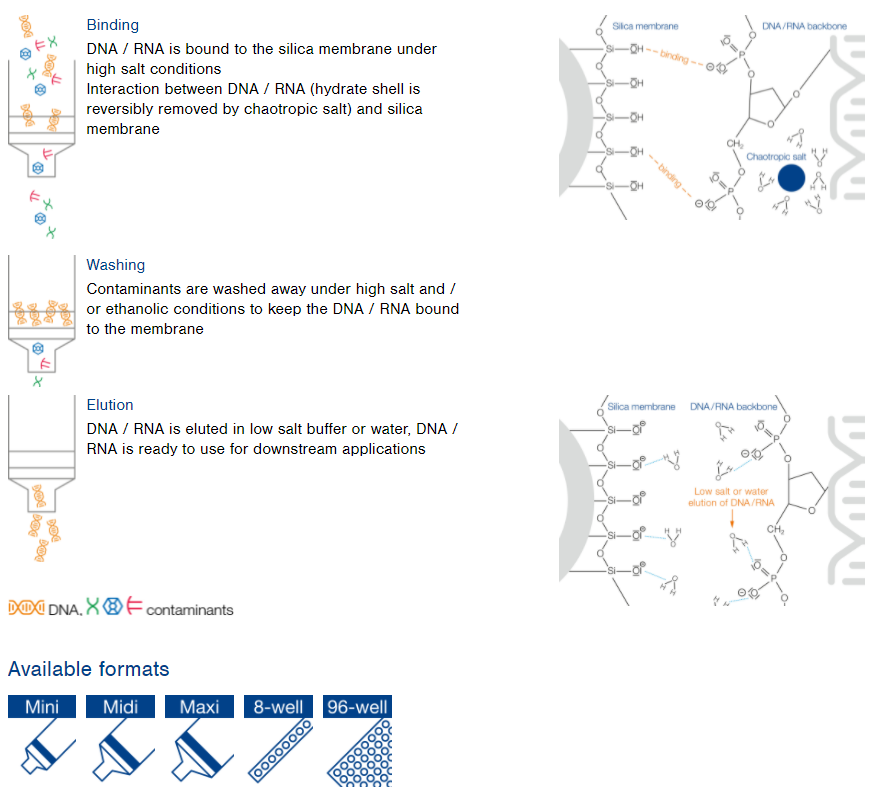
NucleoSpin technology
Rapid and easy preparation of DNA and RNA
Features
- Chaotropic salt based silica membrane purification
- Tailored purification systems for low (single columns), medium (8‑well strips) or high throughput (96‑well plates) approaches
- Easy procedure from extra small (XS) to large scale (Maxi)
NucleoSpin principle
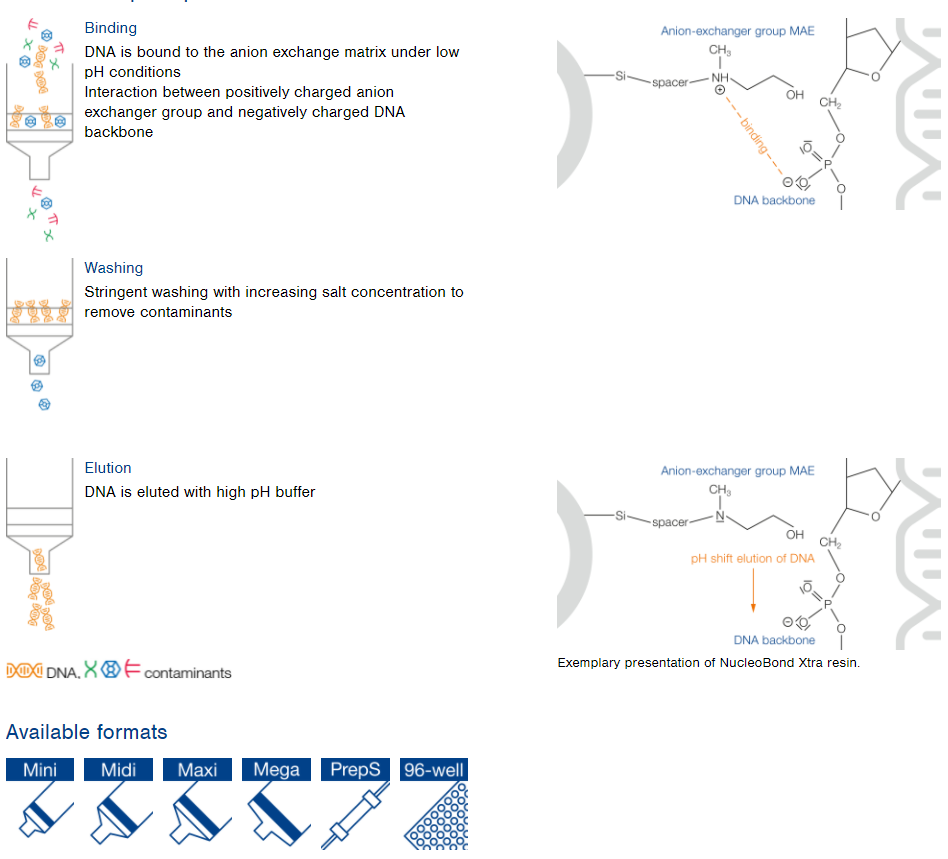
NucleoBond Xtra / PC technology
Highest DNA purity for plasmid DNA purification
Features
- Solid phase anion exchange chromatography
- Modified, macroporous silica gel with MAE (methylaminoethanol) as positively charged functional anion exchanger group
- Gravity flow columns: Mini, Midi, Maxi, Mega, Giga, 96-well plate, and preparative scale
NucleoBond principle
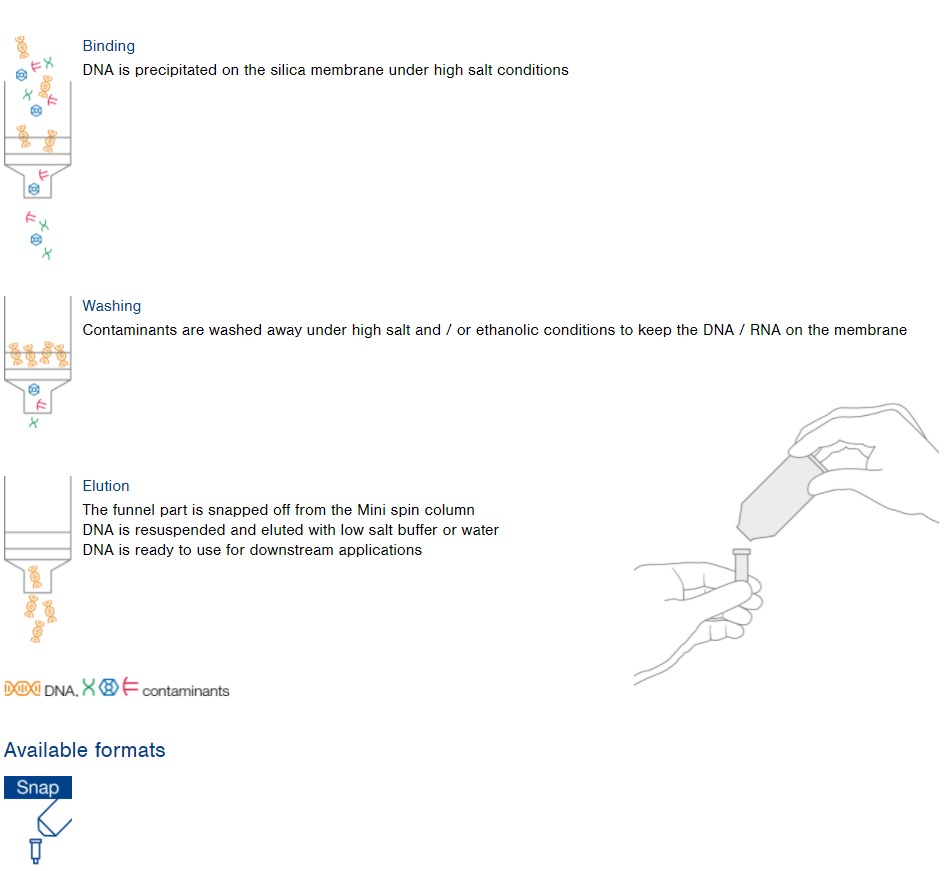
NucleoSnap technology
Vacuum processing of large sample volumes
Features
- Chaotropic salt supported precipitation and filtration
- Snap off column design to process large sample volumes easily
NucleoSnap principle
Let us deliver the latest news to you
We have created a low-volume (not-spammy) newsletter so that you can easily keep up with what's going on in the industry.